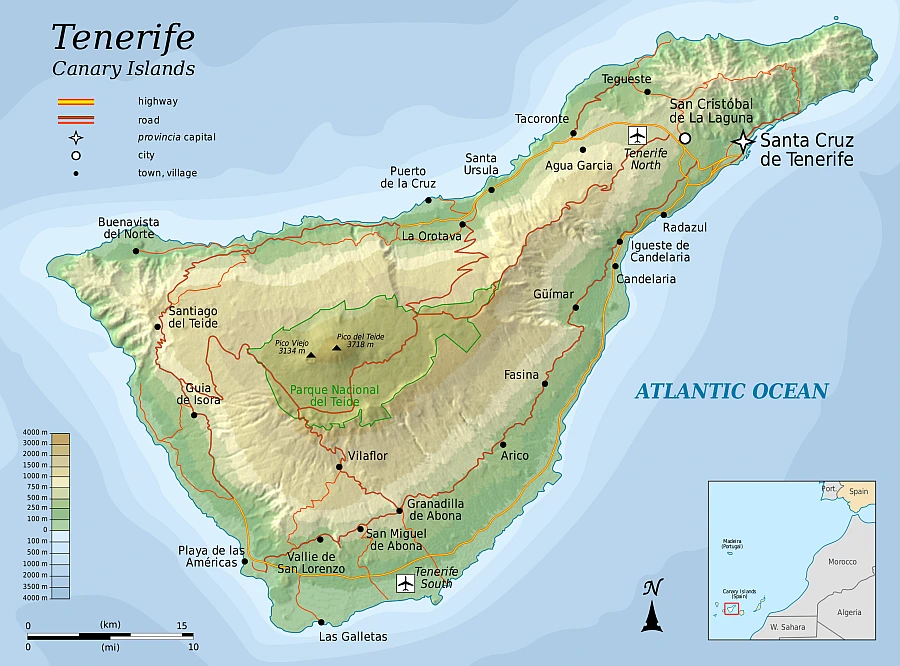
This detailed topographic map of Tenerife provides a comprehensive view of the island’s diverse terrain and key geographical features. The map showcases the island’s unique topography, ranging from the rugged coastline to the towering Mount Teide, the centerpiece of the island’s landscape.
Key Features of the Map:
- Mount Teide: Dominating the central part of the island, Mount Teide is clearly marked as the highest point on the map. Its impressive elevation and the surrounding Teide National Park are well-represented, highlighting the mountain’s geographical significance and role as a tourist attraction.
- Coastline and Beaches: The map outlines Tenerife’s extensive coastline, featuring both rocky shores and sandy beaches. The diverse coastal geography makes it a popular destination for beach-goers and nature enthusiasts.
- Municipal Boundaries: The map delineates the boundaries of various municipalities across Tenerife, providing a clear understanding of the island’s administrative divisions. This feature is particularly useful for understanding local governance and population distribution.
- Road Networks and Urban Areas: Major roads and highways are marked, connecting key urban centers and tourist destinations. The map provides an excellent guide for navigating the island, particularly for visitors planning to explore different regions.
- Natural Reserves and Parks: Other protected areas and natural parks are indicated besides Teide National Park. These areas are crucial for preserving the island’s biodiversity and natural beauty.
- Altitude and Terrain: The map’s topographic contours give an insight into the island’s varied altitude, from the coastal lowlands to the high central plateau. This variation in terrain contributes to Tenerife’s diverse microclimates and ecosystems.
- Water Bodies: The map highlights rivers, reservoirs, and other significant water bodies, emphasizing the role of water in the island’s ecosystem and its importance for agriculture and daily life.
Utility of the Map:
This topographic map is invaluable for tourists, educators, researchers, and locals. It offers a detailed and accurate representation of Tenerife’s landscape, making it ideal for planning excursions, educational purposes, environmental studies, and understanding the island’s natural and cultural heritage.
Location Map of Tenerife
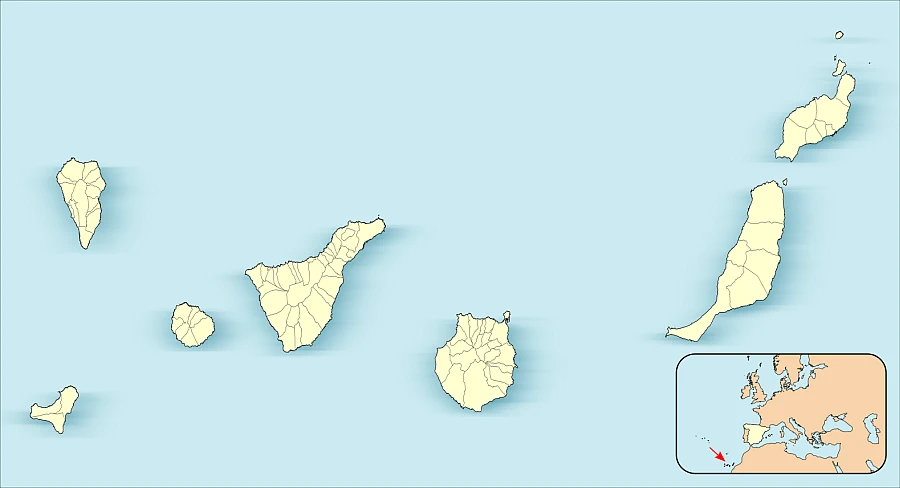
This location map clearly illustrates Tenerife’s position as part of the Canary Islands, an archipelago of Spain situated in the Atlantic Ocean. Tenerife is depicted prominently, centered among the group of islands that make up the archipelago, highlighting its status as the largest of the Canary Islands. Learn more about the location of Tenerife.
Interesting Geographical Facts of Tenerife
- Mount Teide: At 3,718 meters (12,198 feet) above sea level, Mount Teide is not only the highest point in Tenerife but also the highest point in Spain and the third-highest volcano in the world when measured from its base on the ocean floor. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and the centerpiece of Teide National Park, Europe’s most visited national park.
- Diverse Landscapes: Tenerife is often called the “Island of Eternal Spring” due to its varied landscapes and climates. The island features everything from dry, volcanic landscapes in the south to lush, verdant forests in the north. The Anaga Mountains in the northeast are particularly known for their ancient laurel forests.
- Unique Beaches: The island’s coastline is marked by various beaches, ranging from the black volcanic sand beaches of Playa Jardín in Puerto de la Cruz to the golden sands of Playa de las Teresitas near Santa Cruz.
- Microclimates: The topography of Tenerife creates several microclimates. The island’s north often experiences more cloud cover and rainfall, fostering lush greenery. At the same time, the south tends to be drier and sunnier, making it popular with tourists seeking beach vacations.
- Volcanic Origin: Tenerife is the largest of the Canary Islands and has a volcanic origin. The island’s terrain is dotted with various volcanic features, including craters, lava flows, and vents, offering a fascinating insight into its geological history.
- Natural Reserves: Besides Teide National Park, Tenerife is home to several other natural reserves and protected areas, such as the Masca Valley, Teno Rural Park, and the cliffs of Los Gigantes, each offering unique landscapes and wildlife.
- Water Bodies: The island has a complex system of barrancos (ravines), which are dry most of the year but can carry water during periods of heavy rain. These natural features are crucial to the island’s hydrology and unique ecosystems.
- Tenerife’s Size: Covering an area of 2,034 square kilometers (785 square miles), Tenerife is not only the largest of the Canary Islands but also the most populous, with a diverse population that contributes to the island’s vibrant culture.
These geographical facts provide a glimpse into the extraordinary diversity and natural beauty of Tenerife, making it a fascinating subject for study and exploration. The island’s varied terrain and unique features offer endless opportunities for discovery and adventure.